Function
ex)
//1. Function declaration
//function name(param1, para2) { body... return; }
//one function === one thing
//naming: doSomething, command, verb
//e.g. createCardAndPoint -> createCard, createPoint
//funcion is object in JS
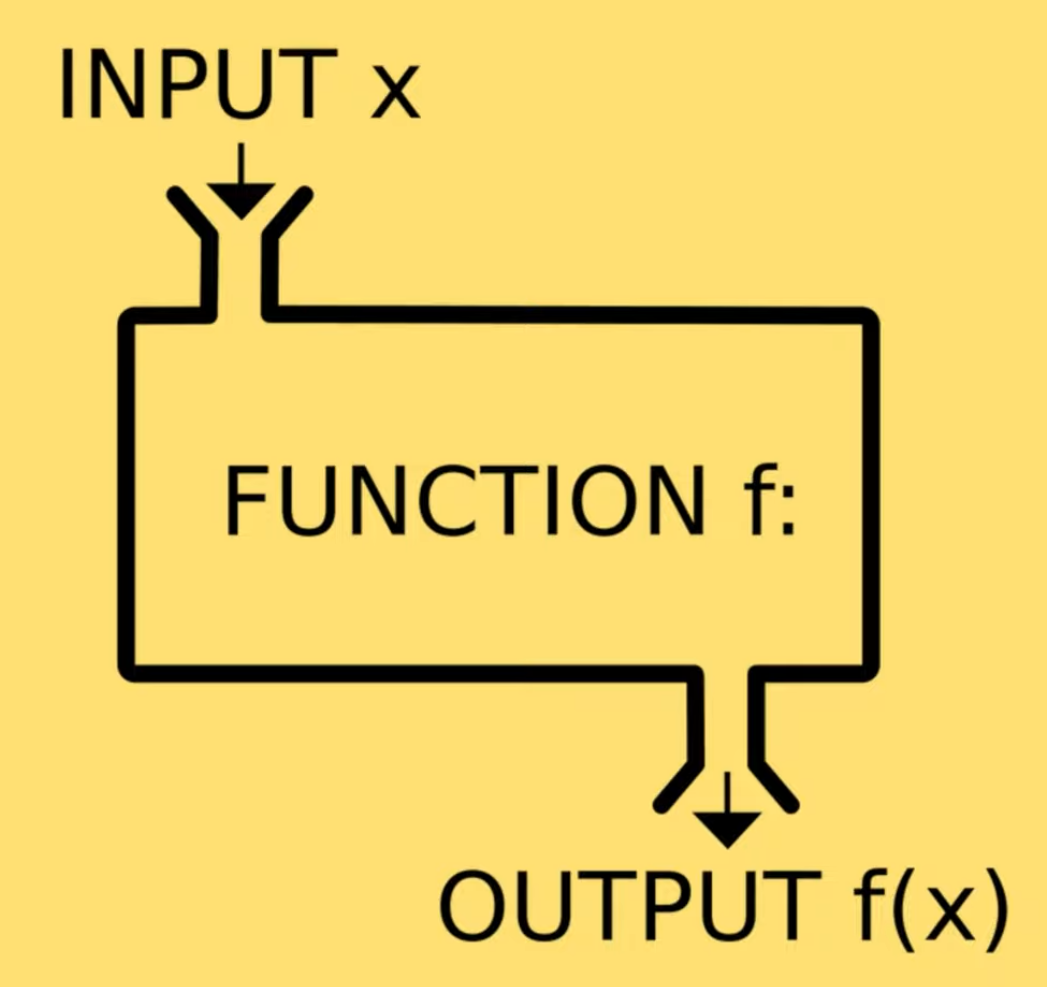
function printHello(){
console.log('Hello');
}
printHello();
function log(message){
console.log(message);
}
log('Hello@');
log(123);
ex)
//2.Parameters
//premitive parameters: passed by value
//object parameters: passed by reference
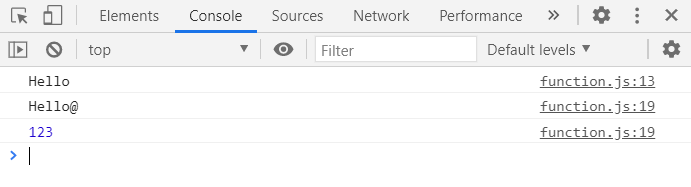
function changeName(obj){
obj.name = 'coder';
}
const ellie = {name: 'ellie'};
changeName(ellie);
console.log(ellie);
ex)
//3. Defalut parameters(added in ES6)
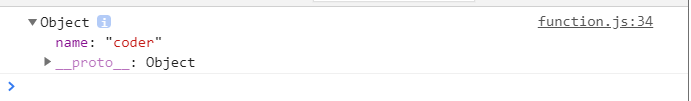
function showMessage(message, from){
console.log(`${message} by ${from}`);
if(from === undefined){
from = 'unknown';
}
console.log(`${message} by ${from}`);
}
showMessage('Hi!');
function showMessage2(message, from = 'unknown'){
console.log(`${message} by ${from}`);
}
showMessage2('Hi!');
ex)
//4. Rest parameters(added in ES6)
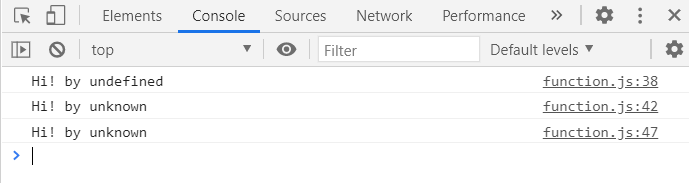
function printAll(...args){
for(let i = 0; i <args.length; i++){
console.log(args[i]);
}
for(const arg of args){
console.log(arg);
}
args.forEach((arg) => console.log(arg));
}
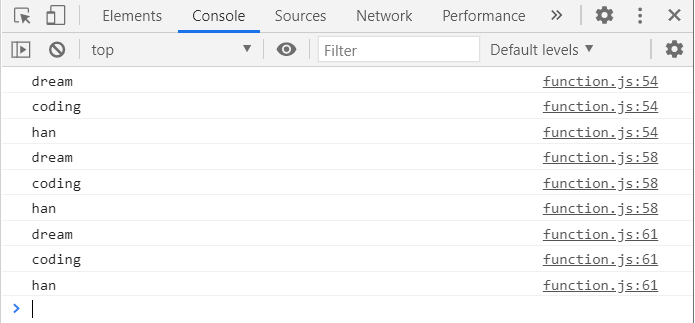
printAll('dream','coding','han');
ex)
//5.Local scope
//밖에서는 안을 볼 수 없고 안에서는 밖을 볼 수 있다.
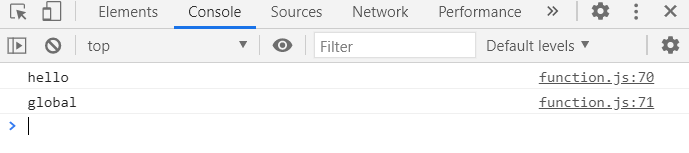
let globalMessage = 'global'//global variable
function printMessage(){
let message = 'hello';
console.log(message); // local variable
console.log(globalMessage);
function printAnother(){
console.log(message);
let childMessage = 'hello';
}
//console.log(childMessage);//에러
}
//console.log(message);//에러
printMessage();
ex)
//6. Return a value
function sum(a,b){
return a+b;
}
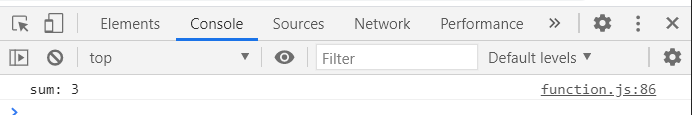
const result = sum(1,2);//3
console.log(`sum: ${sum(1,2)}`);
//7. Early return, early exit
//bad
function upgradeUser(user){
if(user.point > 10){
//long upgrade logic...
}
}
//good
function upgradeUser2(user){
if(user.point <= 10){
return;
}
//long upgrade logic...
}
ex)
//First-class function
//functions are treated like any other variable
//can be assigned as a value to variable
//can be passed as an argument to other functions.
//can be returned by another function
//1.Function expression
//a function declaration can be called earlier than it is defined.(hoisted)
//a function expression is created when the execution reaches it.
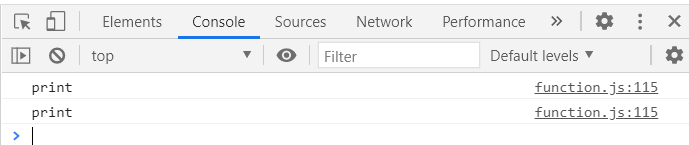
const print = function(){
//anonymous function
console.log('print');
};
print();
const printAgain = print;
printAgain();
ex)
//2. Callback function using function expression
function randomQuiz(answer, printYes, printNo){
if(answer === 'love you'){
printYes();
}else{
printNo();
}
}
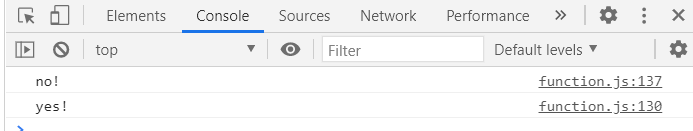
const printYes = function(){
console.log('yes!');
}
//named function
//better debugging in debugger's stack traces
//recursions
const printNo = function print(){
console.log('no!');
//print();
}
randomQuiz('wrong',printYes,printNo);
randomQuiz('love you',printYes,printNo);
ex)
//Arrow function
//always anonymous
const simplePrint = function(){
console.log('simplePrint!');
}
const simplePrint2 = () => console.log('simplePirnt!');
const add = (a,b) => a+b;
const simpleMultiply = (a,b) =>{
//do something more
return a*b;
};
//IIFE: Immediately Invoked Function Expression
(function hello(){
console.log('IIFE');
});'인터넷강의 > 자바스크립트' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 오브젝트 (0) | 2020.09.14 |
|---|---|
| 클래스와 오브젝트의 차이점(class vs object), 객체지향 언어 클래스 정리 (0) | 2020.09.14 |
| 코딩의 기본 operator, if, for loop, 코드리뷰 팁 (0) | 2020.09.11 |
| 데이터타입, data types, let vs var, hoisting (0) | 2020.09.11 |
| 콘솔에 출력, 환경설정, script async 와 defer의 차이점 및 앞으로 자바스크립트 공부 방향 (0) | 2020.09.07 |